Kuri Chhu
| Kuri Chhu | |
|---|---|
 | |
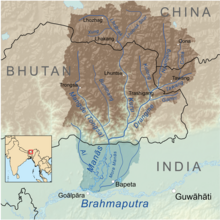 Kuri Chhu (centre) | |
| Location | |
| Country | Bhutan |
| Basin features | |
| River system | Manas River, Brahmaputra River |

The Kuri Chhu, also known as the Lhozhag Xung Qu (tib. lho brag gzhung chu) or Norbu Lag Qu (tib. nor bu lag chu), is a major river of eastern Bhutan, that has formed a scenic valley with high peaks and steep hills. Kuri Chhu is a tributary of the Manas River system, which is the largest river of Bhutan and a major tributary of the Brahmaputra River that drains most of eastern Bhutan.[1]
Course
[edit]The Kuri Chhu originates from the Kula Kangri Glacier in the Tibet Autonomous Region of People's Republic of China where it is known as the Lhozhag Nub Qu (Tibetan: lho brag nub chu, Roman Dzongkha: Lhobrak Chhu) and Xung Qu (Tibetan: gzhung chu), and another origin is the Lhozhag Xar Qu (Tibetan: lho brag shar chu) a.k.a. Damxoi Xung Qu (tib. gtam zhol gzhung chu) originates between the Xoijin Qênri and the Tar Lhari.[2][3] It crosses into Bhutan at a relatively low elevation of 1,200 metres (3,900 ft),[3] flowing in a southerly direction up to Nye and changes its course to south-easterly until it reaches Lhuentse Dzong. Further downstream the Kuri Chhu flows in a south-westerly direction and joins the Manas River.[4]
Tributaries
[edit]The main tributaries of the Kuri Chhu are the Khoma Chhu, Tangkhar Chhu, the Chuneygang Chhu, the Kilung Chhu, the Rong Chhu, the Nye, and Bagang Chhu and the Dungkhar Chhu.[4]
Topography
[edit]Geographically Bhutan forms a giant natural staircase. Starting from the plains of India, in the south, at an altitude of around 100 metres (330 ft), the elevation rises to the high Himalayan peaks of over 7,000 metres (23,000 ft), in the north, on the borders with Tibet. Eastern Bhutan lies across the Donga range running north–south across the country and is crossed by the 3,780-metre (12,400 ft) high Thrumshingla pass. From this high pass the terrain drops precipitously to the low valleys of the Kuri Chhu.
On a clear day, one can see Gangkhar Puensum, Bhutan's highest peak, from Thrumshingla pass. After crossing the pass, for a drive to Sengor the road descends about 700 metres (2,300 ft) in 22 kilometres (14 mi). After Sengor the road begins its descent into the Kuri Chhu valley. Numerous waterfalls and streams slide down the sharp cliffs and leap onto the road. In some places the road is critically cut into the side of the vertical cliff. Finally the road leaves Thrumshingla National Park area and emerges into the upper part of the large valley of the Kuri Chhu, lush with bamboos and ferns. The area is also good for bird watching. The winding road gradually descends through corn fields, rice terraces and tropical fruit plants begin to appear. At Zuri Zampa (bridge) it gets to the lowest point at 570 metres (1,870 ft), after a marked descent of about 3,500 metres (11,500 ft) from Thrumshingla Pass[5]
Water sports
[edit]Bhutan is emerging as a noted destination for white water sports, although tourism in the country is strictly regulated. The rivers in Bhutan generally rush down very steep slopes with great force and road access is limited. Therefore, only relatively short sections of the main rivers are suitable for kayaking and rafting. Even within these limitations Bhutan is an attractive destination for the recreational kayaker with incredible rivers that are both challenging and are amongst some of the most beautiful in the world. The Kuri Chhu offers three runs—the 14-kilometre (9 mi) upper run and the 20-kilometre (12 mi) middle run are suitable only for kayaking, but the 10-kilometre (6 mi) lower run is suitable for both rafting and kayaking.[6]
Hydropower
[edit]Bhutan's hydropower potential is estimated at 30,000 MW but harnessed capacity is only 460 MW, which includes the 60 MW run-of-the-river type project commissioned in 2001 on Kuri Chhu in Mongar District.[7][8] Bhutan and India formed Kurichu Project Authority in 1994 to develop a power plant on the Kuri Chhu. A 55-metre (180 ft) straight gravity concrete dam was built with a surface power house operating at average net head of 32 metres (105 ft).[9]
The Kuri Chhu Hydropower Plant is located in Gyalpozhing, in the Mongar District of Eastern Bhutan. The hydropower plant was formally inaugurated by HRH Trongsa Penlop Jigme Khesar Namgyel Wangchuck and H.E Shri Sudhir Vyas, Ambassador of India to Bhutan, on April 26, 2006. The design capacity is 60 MW (4x15 MW).[10]
Weaving
[edit]Some of the villages of traditional "kushitara" weavers, linked with the royal family of Bhutan, are found in the Kuri Chhu valley near Mongar. The entire weaving process for complete kira takes between six months to one year to complete. The Bhutanese prize these textiles so highly that they are considered part of a family's wealth and are used as currency.[11][12]
See also
[edit]- Kurtoed Province, the historical "Upper Kur" province
- Kurmaed Province, the historical "Lower Kur" province
References
[edit]- ^ "Eastern Bhutan" (PDF). Lonely Planet. Archived from the original (PDF) on 2011-06-07. Retrieved 2010-05-09.
- ^ Zürcher, Dieter; Choden, Kunzang (2004). Bhutan, Land of Spirituality and Modernization: Role of Water in Daily Life. New Dawn Press. ISBN 1-932705-43-0.
- ^ a b Brown, L; Mayhew, B; Armington, S.; Whitecross, R. (2007). Bhutan. Lonely Planet. p. 84. ISBN 978-1-74059-529-2.
- ^ a b "Environmental Assessment - Lhuntse - Dungkhar Road" (PDF). Royal Government of Bhutan, Ministry of Communications, Division of Roads. Retrieved 2010-05-09.
- ^ "Jakar (Bumthang) to Mongar". Wind Horse Tours. Retrieved 2010-05-09.
- ^ "Water Sport in Bhutan". TrekkingBhutan. Retrieved 2010-05-09.
- ^ Tenzin, K. "Potential Development Challenges in the Rivers of Bhutan" (PDF). Canadian Rivers Institute. Retrieved 2010-05-09. [dead link]
- ^ "Regional Hydro-power Resources: Status of Development and Barriers" (PDF). USAID. Retrieved 2010-05-09.
- ^ "Hydroelectric Power Plants in South Asia". Archived from the original on July 18, 2009. Retrieved 2010-05-09.
- ^ "Kurichhu Hydropower Plant". DrukGreen.|
- ^ "Eastern of Bhutan". Asia Planet. Archived from the original on 2011-07-23. Retrieved 2010-05-09.
- ^ "Bhutan travel tips". Asia Planet. Retrieved 2010-05-09.

